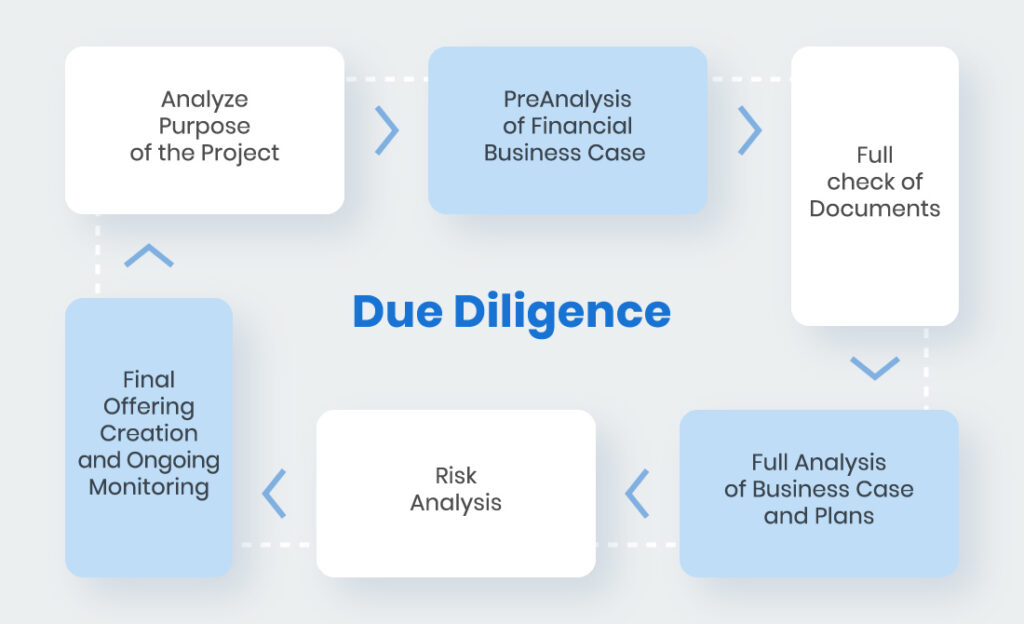
Due Diligence

Due Diligence
Due diligence refers to the process of conducting thorough research, investigation, and analysis before making a decision or taking action. It is commonly used in legal, financial, and business contexts to ensure that all relevant information is considered and risks are minimized.
1. Risk Mitigation: Conducting due diligence helps identify potential risks associated with an investment or business opportunity. By thoroughly examining all aspects of the opportunity, individuals or organizations can assess the likelihood and impact of various risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
2. Informed Decision-Making: Due diligence provides the necessary information and insights for making informed decisions. By gathering relevant data and conducting analysis, decision-makers can better understand the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the opportunity under consideration.
3. Legal Compliance: Due diligence ensures that individuals and organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements. By examining legal documents, contracts, and other relevant information, stakeholders can identify any legal issues or compliance concerns that need to be addressed before proceeding with the investment or business transaction.


4. Financial Evaluation: Conducting financial due diligence allows stakeholders to assess the financial health and performance of a company or investment opportunity. By examining financial statements, cash flows, and other financial metrics, stakeholders can determine the potential returns on investment and evaluate the financial viability of the opportunity.
5. Protecting Stakeholder Interests: Due diligence helps protect the interests of all stakeholders involved in a transaction or investment. By thoroughly examining the terms, conditions, and implications of the opportunity, stakeholders can ensure that their rights and interests are adequately protected and that the transaction is fair and equitable for all parties involved.
Overall, due diligence is essential for minimizing risks, making informed decisions, ensuring legal compliance, evaluating financial performance, and protecting the interests of stakeholders in any business or investment endeavor.
Regulatory Requirement for Due Deligence in India?
In India, various regulatory bodies and laws mandate due diligence requirements in different contexts, particularly in the financial and business sectors. Some of the key regulatory requirements for due diligence in India include:
1. Companies Act, 2013: Under the Companies Act, 2013, companies are required to conduct due diligence when entering into certain transactions, such as mergers, acquisitions, amalgamations, and restructuring. Due diligence is crucial for ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and protecting the interests of shareholders and stakeholders.
2. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Regulations: SEBI regulates securities markets in India and imposes due diligence requirements on various market participants, including listed companies, stock exchanges, merchant bankers, and other intermediaries. SEBI mandates due diligence in processes such as initial public offerings (IPOs), mergers and acquisitions, and takeovers to ensure transparency, investor protection, and market integrity.

3. Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA): FEMA governs foreign exchange transactions and regulations in India. It requires due diligence in cross-border transactions, foreign investments, and external commercial borrowings to prevent money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes.
4. Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Regulations: The RBI regulates banking, financial services, and foreign exchange transactions in India. It imposes due diligence requirements on banks, financial institutions, and other entities to ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system and prevent financial misconduct and fraud.
5. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations: India has enacted various laws and regulations to combat money laundering and terrorist financing activities. Entities such as banks, financial institutions, and intermediaries are required to conduct due diligence on their customers, counterparties, and transactions to identify and report suspicious activities to the authorities.
These are just a few examples of the regulatory requirements for due diligence in India. Depending on the nature of the transaction or activity, other laws, regulations, and regulatory bodies may also impose specific due diligence obligations on individuals and entities operating in India. It’s essential for businesses and investors to stay informed about the relevant regulatory requirements and ensure compliance to avoid legal and regulatory risks.
Why Us?
Singh Suri & Company, Chartered Accountants provide due diligence services as part of their broader range of professional services. Due diligence involves a comprehensive review and analysis of financial, legal, operational, and commercial aspects of a business or transaction. We with their expertise in accounting, auditing, and financial analysis, are well-equipped to conduct due diligence exercises for various purposes, including mergers and acquisitions, investments, financing, and regulatory compliance.
1. Financial Due Diligence: This involves examining the financial records, statements, and performance metrics of a target company to assess its financial health, profitability, cash flows, and potential risks. We analyze financial statements, tax records, budgets, forecasts, and other relevant financial data to identify any discrepancies, anomalies, or red flags.
2. Tax Due Diligence: We review the tax compliance status, strategies, and potential liabilities of the target company to identify any tax-related risks or exposures. This includes analyzing tax returns, assessments, filings, and agreements to ensure compliance with applicable tax laws and regulations.

3. Legal Due Diligence: We collaborate with legal professionals to conduct a thorough review of the legal documents, contracts, agreements, permits, licenses, and regulatory filings of the target company. This helps to identify any legal issues, contractual obligations, litigation risks, or regulatory compliance concerns that may impact the transaction or business operations.
4. Operational Due Diligence: We assess the operational efficiency, capabilities, processes, and management practices of the target company to identify any operational risks, inefficiencies, or opportunities for improvement. This involves analyzing operational metrics, performance indicators, supply chain, production processes, and quality control systems.
5. Commercial Due Diligence: We evaluate the market dynamics, competitive landscape, industry trends, customer relationships, and growth prospects of the target company to assess its commercial viability and strategic fit. This helps investors and acquirers make informed decisions about the potential value and risks associated with the transaction.
Singh Suri & Company, Chartered Accountants play a crucial role in providing objective and independent due diligence services to help clients mitigate risks, uncover hidden issues, and maximize value in business transactions. Our expertise, professional judgment, and attention to detail contribute to the success of due diligence processes and transactions.


