Information system audit

Information system audit
Nowadays, every organization is doing their business with the help of Technology. Information systems form the backbone of all decision support systems with senior management relying heavily on the outputs, reports and business intelligence generated by the Management Information Systems.
Information System Audits (IS Audits) play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity, security, and effectiveness of information systems within organizations. IS audits are essential for maintaining data integrity, safeguarding assets, and achieving organizational objectives.
Information system audits are critical processes aimed at ensuring the integrity, security, and efficiency of information systems within organizations. These audits are conducted to evaluate whether an organization’s information systems are safeguarding assets, maintaining data integrity, and operating effectively to achieve the organization’s objectives.
1. Regulatory Compliance: Information system audits are often governed by various regulatory bodies and standards, such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), and the Information Technology Act, among others.
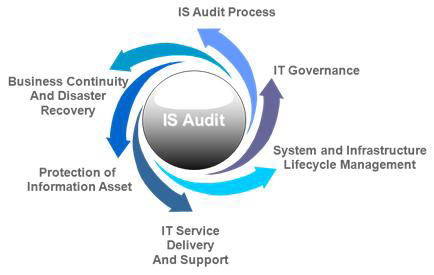
2. Scope: The scope of information system audits typically covers areas such as IT governance, IT security, data management, system development and maintenance, business continuity planning, and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
3. Types of Audits: Information system audits can take various forms, including internal audits conducted by the organization’s internal audit department or external audits carried out by independent audit firms. These audits may also be categorized as general controls audits, application controls audits, or compliance audits.
4. Audit Process: The audit process involves planning, assessing risks, evaluating controls, testing procedures, and reporting findings. Auditors may use various techniques such as interviews, document reviews, observation, and technical testing to gather evidence.
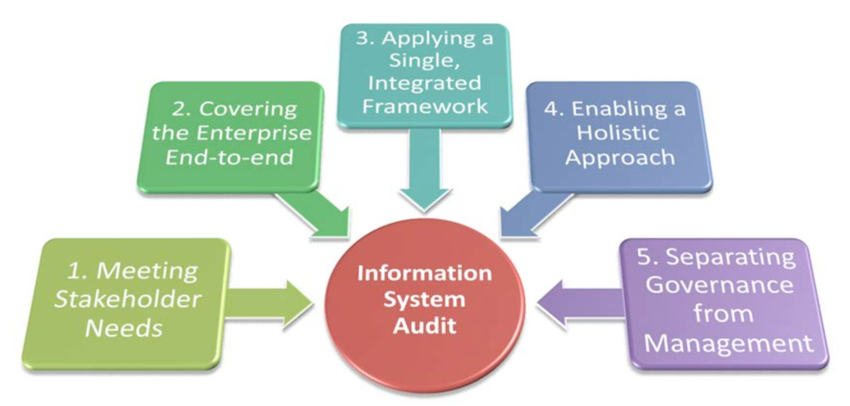
5. Audit Standards: Auditors adhere to established standards and frameworks such as ISACA’s COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies), ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security Management System), and NIST Cybersecurity Framework, among others.
6. Challenges: Information system audits in India face challenges such as rapid technological advancements, evolving cyber threats, complex regulatory requirements, shortage of skilled auditors, and the need for continuous monitoring and updating of audit processes.
7. Importance: Information system audits are essential for identifying weaknesses, enhancing controls, mitigating risks, protecting sensitive information, and maintaining stakeholder trust in an organization’s information systems.
8. Future Trends: With the increasing digitization of businesses and the growing complexity of IT environments, the demand for information system audits in India is expected to rise. Auditors may also need to adapt to emerging technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and blockchain.
Overall, information system audits play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and security of information systems in Indian organizations, helping them adapt to the evolving digital landscape and regulatory requirements.
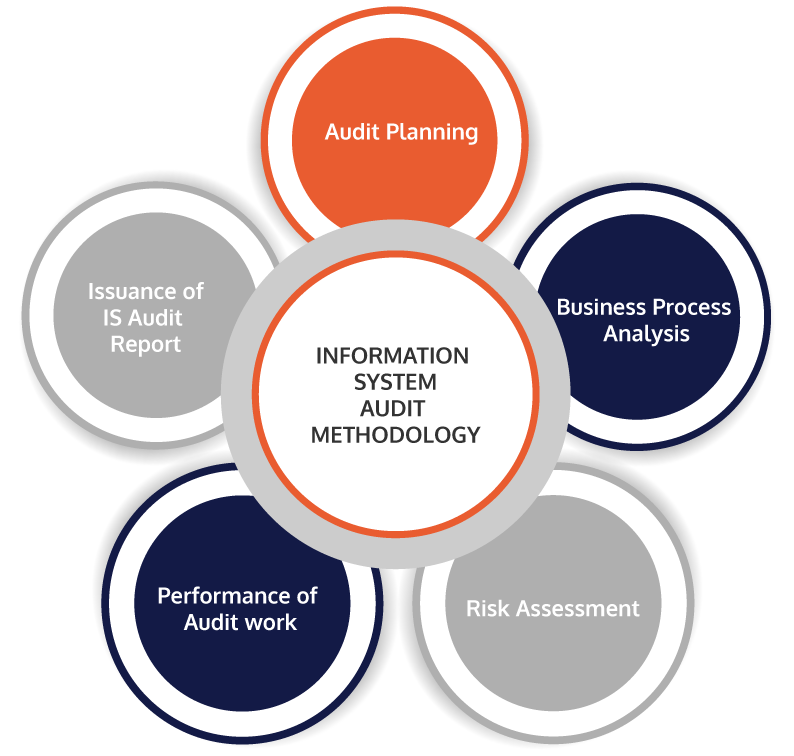
Regulatory Requirement for ISA in India?
In India, the regulatory requirement for Information Systems Audit (ISA) varies depending on the industry, the nature of the organization, and regulatory bodies overseeing specific sectors. Here are some key regulatory requirements for ISA in India:
1. Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The RBI mandates information system audits for banks and financial institutions under its purview. RBI guidelines require banks to conduct regular IS audits to assess the effectiveness of their information systems, cybersecurity measures, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
2. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): SEBI regulates the securities market in India and may require entities such as stock exchanges, brokerage firms, and listed companies to conduct information system audits to ensure the integrity of trading platforms, investor data protection, and compliance with SEBI regulations.
3. Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI): ICAI sets standards for auditing practices in India. It issues guidance on conducting IS audits and provides certification for Information Systems Audit (ISA) professionals through its ISA course. Many organizations in various sectors may voluntarily choose to engage ISA-certified auditors for their information system audits.
4. Information Technology Act (IT Act): The IT Act of India provides a legal framework for electronic transactions, data protection, and cybersecurity. It may require certain organizations to undergo periodic information system audits to ensure compliance with cybersecurity provisions and data protection requirements outlined in the Act.
5. Other Regulatory Bodies: Depending on the industry and sector, other regulatory bodies such as the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI), Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) may also have specific requirements related to information system audits for organizations under their jurisdiction.


6. Industry-Specific Regulations: Certain industries, such as healthcare, telecommunications, and e-commerce, may have sector-specific regulations or guidelines that necessitate information system audits to address industry-specific risks, data protection requirements, and cybersecurity concerns.
Overall, while there may not be a single overarching regulatory requirement for ISA applicable to all organizations in India, various regulatory bodies and industry-specific regulations mandate information system audits to ensure the security, integrity, and compliance of organizations’ information systems with applicable laws and standards. Compliance with these requirements helps organizations mitigate risks, safeguard sensitive information, and maintain trust with stakeholders.
Why Us?
Information system audit services provided by our DISA/CISA qualified Chartered Accountants & Specialised Professionals/Experts, involve the assessment of an organization’s information technology (IT) systems, processes, and controls to ensure they are effective, secure, and compliant with relevant regulations and industry standards. We help organizations identify risks, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses in their IT infrastructure and provide recommendations for improvement.
1. Risk Assessment: We begin by conducting a comprehensive risk assessment of the organization’s IT environment. This involves identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and risks that could impact the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information and IT systems.
2. Audit Planning: Based on the risk assessment, Our team of Experts develop an audit plan outlining the scope, objectives, and procedures for the information system audit. The audit plan considers factors such as the organization’s business objectives, IT infrastructure, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices


3. Review of IT Controls: We assess the design and effectiveness of IT controls implemented by the organization to mitigate identified risks. This includes controls related to access management, data security, change management, system development, and IT governance.
4. Technical Testing: Our Team may perform technical testing of IT systems and applications to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors. This may involve techniques such as penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security assessments of networks, servers, and software applications.
5. Compliance Review: We ensure that the organization’s IT systems and processes comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and ISO/IEC 27001.
6. Data Protection and Privacy: Our Team of Professionals assess the organization’s data protection and privacy practices to ensure compliance with applicable privacy laws and regulations. This includes reviewing data handling processes, data retention policies, data encryption methods, and privacy impact assessments.
7. Reporting and Recommendations: Upon completion of the information system audit, We issue a comprehensive audit report summarizing their findings, observations, and recommendations. The report typically includes an assessment of IT controls, identified deficiencies, and prioritized recommendations for remediation.
8. Follow-Up and Monitoring: Our Team may provide ongoing support to the organization in implementing remediation measures and monitoring the effectiveness of control improvements. This may include conducting follow-up audits or assessments to verify that corrective actions have been implemented satisfactorily

Information system audit services provided by our firm, Singh Suri & Company, Chartered Accountants help organizations enhance the security, reliability, and resilience of their IT infrastructure and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. By conducting thorough assessments and providing actionable recommendations, we assist organizations in mitigating IT risks and achieving compliance with regulatory requirements.


